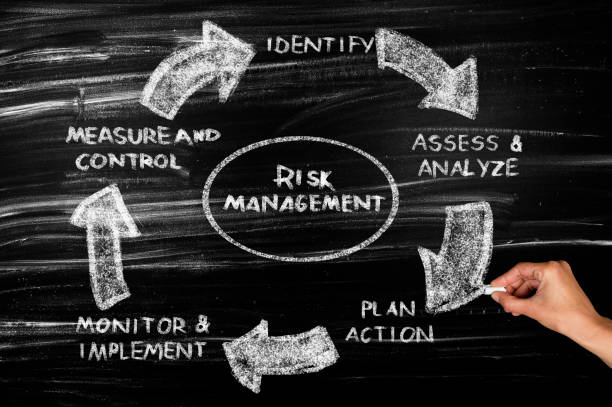
Process of Risk Management in the project and the Elements of Risk Management Implementation, we looked at what a board is at risk and the fundamental components to threatening executives in your association.
In this article, we examine the risk management process, Risk management is the responsibility of the Market & objectives of risk management and how to identify, evaluate, and respond to project prospects.
The Risk management process is a clearly characterized technique for knowing what threats and openings are available, what they may mean for a task or association, and how to respond to them.
Read also:
Fundamental and Process Of Risk Management

① Recognize the Risk
Visualize and capture potential threats to the enterprise. Influence reviews of your undertaking to benefit from related knowledge. Check the built-in driver to find out why an unexpected result occurred.
② Determine the likelihood and impact of the Risk
For each hazard factor, you identify, determine the probability of the hazard event occurring, and evaluate the expected impact assuming the hazard.
③ Plan and Prioritize Opportunities
Since you have the probability and the impact level, settle the final position for each risk factor by combining these two properties. Use a table organization (see Risk Management Matrix below).
The Risk Management Process steps have 4 essential fundamentals:
- Identify the Risk
- Survey the Risk.
- Treat the Threat.
- Monitoring and Report on Risk.
Identify the Risk.
The initial stage in the Danger Board cycle is to isolate each one of the opportunities that may adversely (threat) or certainly (opportunity) affect the goals of the task:
| ‣ Project Achievements |
| ‣ The monetary direction of the undertaking |
| ‣ Project scope |
| ‣ Risk Evaluation |
⦿ These events can be recorded in the hazard grid and later on the hazard list.
A threat (or opportunity) is characterized by its depiction, causes and consequences, subjective assessment, quantitative assessment, and elimination plan.
It can also be described who is accountable for its activity. Each of these characteristics is important for the threat (or freedom) to be valid.
In order to be adequately observed, the identified risk and opportunity (R&O) must be as accurate and clear as can actually be expected. The title of the threat or opportunity should be short, clear, and clearly specific.
All individuals in the undertaking can and must recognize R&O, and the essence of this is the risk (or opportunity) obligation of the owners.
Risk managers are accountable for guaranteeing that proper negotiation is carried out through business with threat owners to identify threats and create a response plan.
We will explain each of these functions in additional detail in our next article on Risk Management Team Roles.
The following are examples of tools to help differentiate R&O:
- Check existing documents
- Interview with experts
- Leading Conceptual Assembly
- Using the methodology of standard strategies – such as failure mode, effects and critical analysis (FMECA), cause trees, and so on
- Taking into account the examples derived from R&O experienced in previous projects
- Using a pre-determined agenda or survey covering different places of work (Risk Breakdown Structure or RBS).
Risk Identification is the first step in Risk management.
Threat identifiable evidence empowers organizations to promote an intention to limit catastrophic opportunities before they emerge.
The goal of this progress is to identify all potential threats that could harm an organization’s operations, for example, claims, robberies, innovation breaks, business downturns, or even a Category 5 hurricane.
Experts in security officers should understand that threat ID is certainly not a one-time process. Considering everything, the chakra has to be perfect, smart, and progressive.
Ways to Identify risks
Despite there being many ways to recognize association hazards, a portion of the more general models include conceptualizing, thinking critically, and seeking representative input.
① Conceptualizing: Risk administrators can track how likely conceptualizing different catastrophic opportunities with other organization partners, such as directors and some C-level employees, can help isolate new threats.
② Pessimistic Thinking: The well-being of executives involves being prepared for the direst while regularly hoping for the best in a career.
Despite the fact that negativity in the work environment is often not overpowering, separating the effort from considering “what is the worst thing that can happen to an organization” can be useful in isolating threats.
③ Seek employee feedback: A high-level administration’s view of the dangers of a union can be strikingly unique in relation to workers’ perspectives.
Workers may experience new hazards in their daily practice that may not have been experienced in any case. For example, a lack of preparation on a piece of working gear can put employees at risk of injury.
All things considered, workers are an invaluable source of direct data.
‣ Important Note: As mentioned earlier, the final progress in the Risk Identification process is for opportunities to screen and audit, as some threats will be available forever. Using the catastrophic event model, organizations in Florida would be at perpetual risk of a tornado attack, although organizations in specific fragments of Kansas would be in perpetual danger of being hit by cyclones.
Survey the Risk
There are two types of risk and opportunity assessment: subjective and quantitative. A subjective assessment dissects the degree of significance dependent on the possibility and impact of the opportunity.

A quantitative assessment breaks down the monetary impact or benefit of the opportunity. Both hazards and openings are important for a comprehensive assessment.
① Subjective assessment
Risk owners and risk managers will rank and focus the probability and impact of the event by severity on each recognized threat and opportunity, as indicated by the scale of the criticality of the task.
Estimation of Probability of Event (P):
Still in the air is ideally dependent on experience, the progress of the task, or, in all likelihood, by addressing a threat master and is close to 100% in size to 1.
For example, consider the threat that: “Provider X’s powerlessness to lead a study on a change Y before the end of 2025 is half as likely”. It is still up in the air from the input and examination of the risk management is responsibility of the of the provider.
Assessments Affecting Severity (I):
To evaluate the general effect, it is important to evaluate the severity of each of the described effects at the work level. A scale is used to sort the different effects and their severity. This guarantees that the assessment of threat and opportunity is normalized and reliable.
The critical level of risk or opportunity is achieved by the situation: Severity = P x I
The reason for the subjective evaluation is to guarantee that the threat supervisory group first focuses on responding to the basics.
② Quantitative assessment
In many ventures, the goal of quantitative valuation is to establish a monetary assessment of the impact of a threat or the benefit of an opportunity, should it be a good idea to do so.
This progress is made by the risk owner, a risk manager (with the help of people responsible for assessment and statistics), or the governance regulator dependent on the official system in the organization.
These amounts address an expected additional expense (or a potential benefit assuming we are discussing an opportunity) that is not expected in the work expense plan.
For this, it is Fundamental along these lines:
① To estimate the additional expenses due by looking at it monetary:
- Long term interior designing
- long term subcontracting
- extra work to do
- Changes to Contracts and Additional Claims
- And so on
② Finding out the effect of unwanted opportunity by combining these properties.
- This progress will enable an assessment of the risks and prospects of the undertaking for the need for an additional spending plan.
Why Assess Risk?
- Identifying weak areas inside a particular unit.
- Successfully syncing assets. can be spent on such a large number of persons or too much time Procedures that do not require so much attention while ‘more dangerous’ procedures are lacking thoughtlessness
- To express possibilities – a complete result that will outwardly show you above and beyond the board is where the issues are.
‣ Important Note: Risk assessments may be performed on a single potential within a critical capacity, or they may Can be performed at a significant capacity inside a large division. On the accompanying pages is a the layout of a hazard assessment review that can be applied to a more modest entity (slightly) tweaking) or an entire partition.
Treat the threat.
To treat threats, an association must initially differentiate its procedures for doing so by promoting a treatment plan.

The goal of a hazard treatment plan is to reduce the likelihood of a hazard event (preventive activity) as well as the effect of a hazard (mitigation activity).
For a chance, the goal of the treatment plan is to improve the chance of occurrence as well as to build on its benefits. Characterized by a response method to the enterprise, based on the consideration of threat or opportunity.
Together 7 ways are conceivable:
Accept:
Try not to start any activity yet keep observing.
Reducing/increasing:
Reducing (for danger) or increasing (for chance) the severity of the impact along with the probability of the event.
Transfer/Share:
Transfer hazard liability to an outsider who can bear the consequences of the issue (share the benefits of an accepted opportunity).
Avoid / Exploit:
Dispose of vulnerabilities completely / Jump at every opportunity.
It is the responsibility of the hazard owner to monitor the progress of the treatment plan. They should continuously report to the Hazard Supervisor, who should keep up with the latest.
Note: The expense of the risk mitigation plan should be coordinated into the expenditure plan of the undertaking.
When characterizing the treatment plan:
- Every activity begins with an action verb word and has a proper reason.
- Each activity has an action and a cutoff time.
- The cost-generating activities in the undertaking should be followed and considered.
- For example: To reduce the risk of my vehicle stalling, a treatment plan might be to have it checked out by an auto shop every year.
When exactly does chance turn into an issue?
Line chart showing the particular moment at which a threat turns into an issue
It is conceivable that, regardless of the activities established to relieve or prevent it, the probability of danger may increase and reach 100%. When the threat is confirmed, we currently don’t see it as a threat but as an issue.
The risk manager must then illuminate the various undertaking partners who will convert that threat into an issue and move it to the issue log.
Monitoring and Report on Risk
A threat report gives data about what the organization is most likely to squeeze into at the moment. Typically, this will address basic threats,
Where the implications for the firm may be significant; also as emerging hazards that may later lead to great difficulty assuming they have not been carefully examined.
Also, the threat report should state how well the organization is doing or alternatively not dealing with those threats at the time.
So the report may also include material on which methods are lacking, which controls are not working as expected, of course, additional progress may be important to stay with the risk inside resistance levels.
Why risk reporting is Important?
Major, the lack of mechanisms is significant on the grounds that the governing body’s risk management is responsibility of the to examine the threat feasibility of the executive’s structure—and that the board (apparently the review council) does not bode well for the organization’s threats without actually getting it.
Can do Review councils that employ lazy tactics to monitor threats, officials disregard their guardianship obligations under the law and may face claims in court.
It is therefore not unexpected that review boards of trustees like to see efficient, viable threat declarations.
Risk disclosure is also important because it helps provide important guidance to the board. For example, your hazard report may warn of a higher risk of disengagement if the organization ventures into developing business areas.
That report may prompt the Board to reconsider whether the extension is prudent, or an alternative assessment technique, or some other step. Despite this, the hazard report is the natural substance used by the Board to consider those decisions.
In the meantime, the supervisory team will rely on the hazard report to see how it may need to change activities to operate in a more dangerous manner. Suppose the board concludes that enterprise is necessary for developing business areas.
It then, at that point, goes to the board to choose how to accomplish that level of leadership.
An in-depth threat report will help senior leaders see how they should refresh strategies regarding gift and diversion expenses, or motivation remuneration to hit deals shares or an appropriate easing framework for examining clients abroad. may have to.
Gift and Entertainment Compliance Powerful threat declaration is also important for controllers.
Whether it would be appropriate for them to visit your organization at some point to directly or consistently audit the program and track down their weak ability to report and talk about opportunities doesn’t do a good thing.
On the Assessment of Continuity Programs Think about this section of the equity department directive:
Why is a Risk Management Strategy Important?
Project and functional hazards are common to most organizations, yet board cycles and systems are fundamental in recognizing your organization’s merits, shortcomings, openings, and threats (SWOT) – otherwise called directing a SWOT investigation.

There are many different benefits to adequately overseeing opportunities.
① Functional Effectiveness and Business Continuity
No matter how prepared your business is, functional hazards can pop up at any time – and from sources, you may not have previously been aware of.
Threats can manifest as another network security threat, a provider or specialist co-op that is unprepared to support your organization at this time, or a gear frustration.
With each of the moving parts both in and out of an organization that has an impact, a setup is in place to set up a circle of executives at risk and a methodology that allows you to guarantee inward control to prevent misrepresentation.
Provides – or manages – a variety of threats to manage as soon as they emerge.
② Assurance of your company's assets
Whether it is actual hardware, supplies, or data, ensuring that your organization has resources is basic.
A new report from IBM shows that more than 8.5 billion records were compromised in information breaks between April 2019 and 2020 – the super estimated general expense of information breaks was US$3.86 million.
In the one-year time frame ending April 2020, 80 percent of the robberies were client-related truly identifiable data (PII). This creates a strong and notable threat to the system of authorities which is an occupational security approach.
③ Consumer Loyalty and Loyalty
Your organization’s logo, image, enhanced appearance, and notoriety are also a resource – and your customers breathe easier in the light of seeing and interacting with them on a day-to-day basis.
To the point that your business has thoroughly vetted and jeopardized the board plan and implemented it, your customers may feel that everything is good and sure about your notoriety and brand.
Your threat methods and cycles help you protect your image and notoriety by protecting these resources. It also guarantees that customers can maintain confidence in your ability and communicate the items and arrangements that you have submitted.
The result is a more severe level of consumer loyalty and dependability.
④ Accepting Benefits and Achieving Goals
A large part of completing undertakings on time and meeting expected objectives depends on how potentially threatening the risks are.
Threats to board ID, evaluation, and rehearsal of executives quickly uncovers vulnerabilities – and allow your organization to eliminate actions and practices that essentially don’t turn a profit from the enterprise.
This expands your shot of completing your general venture portfolio and achieving more comprehensive trade execution and expected rewards.
⑤ Extended Profitability
The primary concern for most organizations is staying productive.
Often when something like a break happens, there is a considerable monetary impact – and this usually includes hours taken to work with lawful and security groups to lead extended exams.
Monitoring the market, credit, functional, reputation, and various threats are essential to keep your core concern solid.
Important: The cause of Risk to the authorities is not to dispose of all threats. This is to limit the potential adverse outcome of the hazards. By working with risk chiefs, delegates can settle on great hazard options to work on the shot at remuneration.
Fundamental Activities of Risk Management
Risk management is the area that attempts to guarantee that hazards have an impact on cost, quality, and timeliness.
is limited.
The primary reason for board hazards is to isolate and deal with product project-related hazards and to deal with the problem. Assessing hazards that may affect enterprise planning or the nature of the product being manufactured and taking steps to avoid hazards is an important undertaking of a Director of Operations.
Risks are called executives to distinguish and plan for the purpose of mitigating their impact on the job. The main motivation of danger to the authorities is to stay away from disaster or great misfortune.
‣ The Risk can be arranged as follows.
① Project Risk:
These are hazards that affect the time schedule or assets of the undertaking.
② Item Risk:
These are hazards that affect the quality or performance of what is created.
③ Business Risk:
These are hazards that affect the association that manufactures or receives the product.
FAQ [frequiently Asked Question]
What is The risk management process?
Process of Risk Management in Project of Risk Management and the Elements of Risk Management Implementation, we looked at what a board is at risk and the fundamental components to threatening executives in your association.
In this article, we examine the risk management process, Risk management is the responsibility of the Market & objectives of risk management and how to identify, evaluate, and respond to project prospects.
The risk management process is a clearly characterized technique for knowing what threats and openings are available, what they may mean for a task or association, and how to respond to them.
How do Identify the Risk?
The initial stage in the Danger Board cycle is to isolate each one of the opportunities that may adversely (threat) or certainly (opportunity) affect the goals of the task:
‣ Project Achievements
‣ The monetary direction of the undertaking
‣ Project scope
‣ Risk Evaluation
Why is a Risk Management strategy important?
Project and functional hazards are common to most organizations, yet board cycles and systems are fundamental in recognizing your organization’s merits, shortcomings, openings, and threats (SWOT) – otherwise called directing a SWOT investigation.
There are many different benefits to adequately overseeing opportunities.
① Functional Effectiveness and Business Continuity
No matter how prepared your business is, functional hazards can pop up at any time – and from sources, you may not have previously been aware of.
Threats can manifest as another network security threat, a provider or specialist co-op that is unprepared to support your organization at this time, or a gear frustration.
With each of the moving parts both in and out of an organization that has an impact, a setup is in place to set up a circle of executives at risk and a methodology that allows you to guarantee inward control to prevent misrepresentation.
Provides – or manages – a variety of threats to manage as soon as they emerge.
Why risk reporting is important?
Major, the lack of mechanisms is significant on the grounds that the governing body’s risk management is responsibility of the to examine the threat feasibility of the executive’s structure—and that the board (apparently the review council) does not bode well for the organization’s threats without actually getting it.
Can do Review councils that employ lazy tactics to monitor threats, officials disregard their guardianship obligations under the law and may face claims in court.
It is therefore not unexpected that review boards of trustees like to see efficient, viable threat declarations.
Risk disclosure is also important because it helps provide important guidance to the board. For example, your hazard report may warn of a higher risk of disengagement if the organization ventures into developing business areas.
That report may prompt the Board to reconsider whether the extension is prudent, or an alternative assessment technique, or some other step. Despite this, the hazard report is the natural substance used by the Board to consider those decisions.
What are the main activities of risk management?
Risk management is the area that attempts to guarantee that hazards have an impact on cost, quality, and timeliness.
is limited.
The primary reason for board hazards is to isolate and deal with product project-related hazards and to deal with the problem. Assessing hazards that may affect enterprise planning or the nature of the product being manufactured and taking steps to avoid hazards is an important undertaking of a Director of Operations.
Risks are called executives to distinguish and plan for the purpose of mitigating their impact on the job. The main motivation of danger to the authorities is to stay away from disaster or great misfortune.
Related Terms
- Importance of Sales Management
- Important Functions of Sales Management
- What is Sales Management?
- Explain the Nature and Scope of Financial Management
- Most Importance of management Control | Management activities
- The Most Important Features of Management | 7 Characteristics of Management
- Bank Management
Summary & Conclusion
The Process Risk Management Negotiation is a system of steps that you must take on a regular basis, in order to survey and moderate the risks present in your association and lines of business.
It should be essential to your connected way of life. It should become routine for your organization to consider all things to look left and right for a person before crossing the street.
It should be a cycle because it may take some pushing to get where you need to be and moreover depending on how things change after a while. Threat and relief to officers is not a task, yet a constant piece of versatility.
Most organizations must conduct their hazards survey once every year based on the pace of progress in their union, region, and climate.
Like this information Or have something to share!
Connect with us on Facebook